Guidelines for Prevention
1. Don't use tobacco
|
Using any type of tobacco puts you on a collision course with cancer. Smoking has been linked to various types of cancer — including cancer of the lung, bladder, cervix and kidney. And chewing tobacco has been linked to cancer of the oral cavity and pancreas. Even if you don't use tobacco, exposure to secondhand smoke might increase your risk of lung cancer.
|
Avoiding tobacco — or deciding to stop using it — is one of the most important health decisions you can make. It's also an important part of cancer prevention. If you need help quitting tobacco, ask your doctor about stop-smoking products and other strategies for quitting.
2. Eat a healthy diet
|
Although making healthy selections at the grocery store and at mealtime can't guarantee cancer prevention, it might help reduce your risk. Consider these guidelines:
|
- Limit fat. Eat lighter and leaner by choosing fewer high-fat foods, particularly those from animal sources. High-fat diets tend to be higher in calories and might increase the risk of overweight or obesity — which can, in turn, increase cancer risk.
- If you choose to drink alcohol, do so only in moderation. The risk of various types of cancer — including cancer of the breast, colon, lung, kidney and liver — increases with the amount of alcohol you drink and the length of time you've been drinking regularly.
3. Maintain a healthy weight and be physically active
|
- Adults who participate in any amount of physical activity gain some health benefits. But for substantial health benefits, strive to get at least 150 minutes a week of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes a week of vigorous aerobic physical activity. You can also do a combination of moderate and vigorous activity. As a general goal, include at least 30 minutes of physical activity in your daily routine — and if you can do more, even better.
4. Protect yourself from the sun
|
- Cover exposed areas. Wear tightly woven, loosefitting clothing that covers as much of your skin as possible. Opt for bright or dark colors, which reflect more ultraviolet radiation than pastels or bleached cotton.
- Don't skimp on sunscreen. Use generous amounts of sunscreen when you're outdoors, and reapply often.
- Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps. These are just as damaging as natural sunlight.
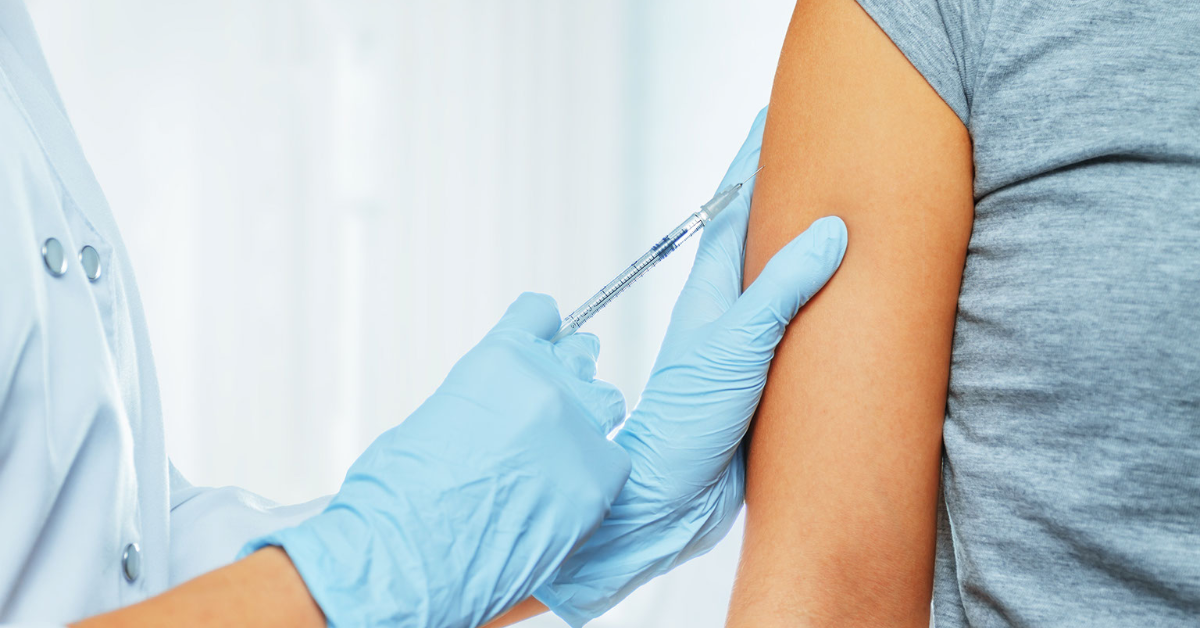
5. Get immunized
Cancer prevention includes protection from certain viral infections. Talk to your doctor about immunization against:
|
- Human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a sexually transmitted virus that can lead to cervical and other genital cancers as well as squamous cell cancers of the head and neck. The HPV vaccine is available to both men and women age 26 or younger who didn't have the vaccine as adolescents.
6. Avoid risky behaviors
Another effective cancer prevention tactic is to avoid risky behaviors that can lead to infections that, in turn, might increase the risk of cancer. For example:
- Practice safe sex. Limit your number of sexual partners, and use a condom when you have sex. The more sexual partners you have in your lifetime, the more likely you are to contract a sexually transmitted infection — such as HIV or HPV. People who have HIV or AIDS have a higher risk of cancer of the anus, liver and lung. HPV is most often associated with cervical cancer, but it might also increase the risk of cancer of the anus, penis, throat, vulva and vagina.
- Don't share needles. Sharing needles with an infected drug user can lead to HIV, as well as hepatitis B and hepatitis C — which can increase the risk of liver cancer. If you're concerned about drug abuse or addiction, seek professional help.
7. Get regular medical care
Take cancer prevention into your own hands, starting today.
The rewards will last a lifetime.
The rewards will last a lifetime.
Warning Signs of Cancer
What Are the Symptoms of Cancer?
In its early stages, cancer may have no symptoms, but eventually a malignant tumor will grow large enough to be detected.
As it continues to grow, it may press on nerves and produce pain, penetrate blood vessels and cause bleeding, or interfere with the function of a body organ or system.
As it continues to grow, it may press on nerves and produce pain, penetrate blood vessels and cause bleeding, or interfere with the function of a body organ or system.
The Seven Warning Signs of Cancer
The American Cancer Society uses the word C-A-U-T-I-O-N to help recognize the seven early signs of cancer:
Change in bowel or bladder habits
A sore that does not heal
Unusual bleeding or discharge
Thickening or lump in the breast, testicles, or elsewhere
Indigestion or difficulty swallowing
Obvious change in the size, color, shape, or thickness of a wart, mole, or mouth sore
Nagging cough or hoarseness
A sore that does not heal
Unusual bleeding or discharge
Thickening or lump in the breast, testicles, or elsewhere
Indigestion or difficulty swallowing
Obvious change in the size, color, shape, or thickness of a wart, mole, or mouth sore
Nagging cough or hoarseness
The following symptoms may also signal the presence of some types of cancer:
- Persistent headaches
- Unexplained loss of weight or loss of appetite
- Chronic pain in bones or any other areas of the body
- Persistent fatigue, nausea, or vomiting
- Persistent low-grade fever, either constant or intermittent
- Repeated infection
Call Your Doctor About Cancer if...
You develop symptoms that may signal cancer, that are specifically not related to another cause, or that persist for more than two weeks. If this occurs, schedule a medical examination. If the cause of your symptoms is cancer, early diagnosis and treatment will offer a better chance of a positive prognosis.